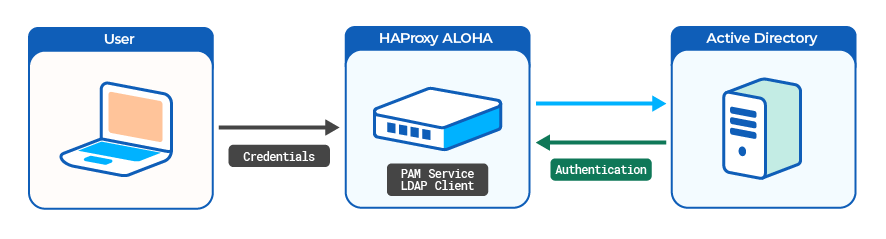
Users and passwords
LDAP authentication
This page applies to:
- HAProxy ALOHA - all versions
System administrators can authenticate to HAProxy ALOHA with a user account defined in an external LDAP server, such as Active Directory Domain Services. You can give each user either administrative access (read/write access) or monitoring access (read-only).
Caution
You’re about to modify how users can log in to HAProxy ALOHA. Before proceeding, connect to the HAProxy ALOHA appliance through SSH, or launch a terminal from the web UI’s Tools tab to avoid being locked out. If you become locked out, restart HAProxy ALOHA to reset your settings.
Prerequisites Jump to heading
Please check that you’ve met the following prerequisites:
- You’re running Windows Server 2008 or later.
- Your Windows Server has the Active Directory Domain Services role and has created an Active Directory forest. See the Windows Server guide Install Active Directory Domain Services.
- Optional: If you plan to use Windows Server as a DNS server, add the DNS Server role. See the Windows Server guide Installing DNS Server.
Enable LDAP authentication Jump to heading
-
HAProxy ALOHA must be able to query the Active Directory DNS server. From the Services tab, click system setup.

-
Enter the name of your AD Domain, and the IP address of the corresponding DNS server.
Option Description dns_domainName of your AD Domain dns_serversIP address of the AD DNS haproxyservice systemhostname ALOHA1rtc utcdns_domain mydomain.comdns_servers 192.168.1.65haproxyservice systemhostname ALOHA1rtc utcdns_domain mydomain.comdns_servers 192.168.1.65Click OK, then Close.
You can also launch the following commands from a terminal:
nixsudo config set system dns_domain mydomain.comsudo config set system dns_servers 192.168.1.65nixsudo config set system dns_domain mydomain.comsudo config set system dns_servers 192.168.1.65 -
From the Setup tab, click Save. Then, click Reboot.
-
To verify that HAProxy ALOHA can communicate with the DNS server, launch a terminal from the web UI’s Tools tab or SSH to your HAProxy ALOHA appliance. Then, query for a DNS hostname within your domain. Here, we call
nslookupto query for the DNS domaindc1.mydomain.com:nixnslookup dc1.mydomain.comnixnslookup dc1.mydomain.comoutputtextServer: 192.168.1.65Address: 192.168.1.65:53outputtextServer: 192.168.1.65Address: 192.168.1.65:53 -
To add LDAP support, go to the Services tab and click pam setup.
-
Add
ldap_auth 1to the PAM service.haproxyservice pamautostartldap_auth 1haproxyservice pamautostartldap_auth 1Tip
To get more verbose logs for easier troubleshooting, specify
debug 1as well. -
Click OK, then Close.
-
Apply your changes to the PAM configuration.
-
Restart the PAM service.
You can also launch the following commands from a terminal:
nixsudo config set pam ldap_auth 1sudo config set pam autostartsudo service pam restartnixsudo config set pam ldap_auth 1sudo config set pam autostartsudo service pam restart -
Create a user account in Active Directory that HAProxy ALOHA will use to connect to the credentials store. If possible, this user should have a password that never expires to avoid any service disruptions. For example, create a user with the account name
alohalogin. -
The HAProxy ALOHA
nslcddaemon queries LDAP based on thenslcd.confconfiguration file. From the Services tab, click nslcd setup.
-
Allow the
nslcddaemon to start automatically by addingautostart.haproxyservice nslcdautostarthaproxyservice nslcdautostartClick OK, then Close.
You can also invoke the following command from a terminal:
nixsudo config set nslcd autostartnixsudo config set nslcd autostart -
In the Services tab, click the [advanced mode] link, then edit the
nslcdconfiguration.
The content of the
/etc/nslcd.confNTP configuration file displays. -
Make the following changes:
-
Set the
uridirective to the address of your LDAP server. For example:nslcd.conftexturi ldap://dc1.mydomain.com/nslcd.conftexturi ldap://dc1.mydomain.com/ -
Set the distinguished name of the search base. For example:
nslcd.conftextbase dc=mydomain,dc=comnslcd.conftextbase dc=mydomain,dc=com -
Set the distinguished name to bind to the server with. For example:
nslcd.conftextbinddn cn=alohalogin,cn=Users,dc=mydomain,dc=comnslcd.conftextbinddn cn=alohalogin,cn=Users,dc=mydomain,dc=comOn Windows Server, you can use the
dquerycommand to get the value:powershellPS C:\Users\admin> dsquery user -samid 'alohalogin'powershellPS C:\Users\admin> dsquery user -samid 'alohalogin'outputtext"CN=alohalogin,CN=Users,DC=mydomain,DC=com"outputtext"CN=alohalogin,CN=Users,DC=mydomain,DC=com" -
Set the credentials to bind with. For example:
nslcd.conftextbindpw mypasswordnslcd.conftextbindpw mypassword -
Uncomment the mappings section for your LDAP server. For Active Directory, it looks like the example below. Replace
DOMAIN_SIDwith theDomainSIDvalue you get from running theGet-ADDomainPowerShell command on your Windows Server.nslcd.conftext# Alternative mappings for Active Directory# (replace the SIDs in the objectSid mappings with the value for your domain)pagesize 1000referrals offidle_timelimit 800filter passwd (&(objectClass=user)(objectClass=person)(!(objectClass=computer)))map passwd uid sAMAccountNamemap passwd uidNumber objectSid:DOMAIN_SIDmap passwd gidNumber objectSid:DOMAIN_SIDmap passwd homeDirectory "/home/$sAMAccountName"map passwd gecos displayNamemap passwd loginShell "/bin/bash"filter group (|(objectClass=group)(objectClass=person))map group gidNumber objectSid:DOMAIN_SIDnslcd.conftext# Alternative mappings for Active Directory# (replace the SIDs in the objectSid mappings with the value for your domain)pagesize 1000referrals offidle_timelimit 800filter passwd (&(objectClass=user)(objectClass=person)(!(objectClass=computer)))map passwd uid sAMAccountNamemap passwd uidNumber objectSid:DOMAIN_SIDmap passwd gidNumber objectSid:DOMAIN_SIDmap passwd homeDirectory "/home/$sAMAccountName"map passwd gecos displayNamemap passwd loginShell "/bin/bash"filter group (|(objectClass=group)(objectClass=person))map group gidNumber objectSid:DOMAIN_SID
Important
Enter a newline at the end of the configuration.
Tip
Other changes you can make to the
nslcd.conffile:- To log
nslcdactions to syslog, specifylog syslog. - To ensure that
nslcddoesn’t fail at startup when the LDAP server is down, specify the AD search base (for example,base dc=mydomain,dc=com). - To minimize latency when a user uses
sudoand the LDAP server is offline, specifynss_initgroups_ignoreusers root,admin,monitor.
-
-
Apply your changes to the
nslcdservice. Then, restart thenslcdservice. -
Verify that HAProxy ALOHA can connect to the LDAP server by testing the connection with the
ldapsearchcommand. This command will prompt you to enter the user’s password. Use these options:Option Description -xUse simple authentication. -hURI referring to the LDAP server. -DDistinguished Name used to bind to the LDAP directory. -WPrompt for password. -bAD search base. nixldapsearch -x -H ldap://dc1.mydomain.com -D alohalogin@mydomain.com -W -b 'CN=Users,DC=mydomain,DC=com'nixldapsearch -x -H ldap://dc1.mydomain.com -D alohalogin@mydomain.com -W -b 'CN=Users,DC=mydomain,DC=com'outputtext# extended LDIF## LDAPv3# base <dc=mydomain,dc=com> with scope subtree# filter: (objectclass=*)# requesting: ALL## mydomain.comdn: DC=mydomain,DC=comobjectClass: topobjectClass: domainobjectClass: domainDNSdistinguishedName: DC=mydomain,DC=cominstanceType: 5whenCreated: 20211202085814.0Z...outputtext# extended LDIF## LDAPv3# base <dc=mydomain,dc=com> with scope subtree# filter: (objectclass=*)# requesting: ALL## mydomain.comdn: DC=mydomain,DC=comobjectClass: topobjectClass: domainobjectClass: domainDNSdistinguishedName: DC=mydomain,DC=cominstanceType: 5whenCreated: 20211202085814.0Z...If the
ldapsearchcommand fails, check your network configuration. -
To make your changes persistent after a reboot, click the Setup tab. Then click Save under Configuration.
The
configuration was successfully savedmessage displays.
You can also launch the following command from a terminal:
nixsudo config savenixsudo config save
Set access rights for users Jump to heading
Users can have either monitor (read-only) or admin (read/write) access. To set a user’s access rights:
-
From the Tools tab, use the file manager to edit the file
/etc/security/users.conf. Add users that have an account on the LDAP server, specifying the following for each:Option Description userSet the Active Directory user account name. auth_typeSet to ldap.serviceSet to one or more of these values: wui(web UI),sshd(SSH), orlogin(console). This restricts how a user can log in.allowordenyEnable or disable the user’s login. map_to_userSet adminfor read/write access ormonitorfor read-only access.Here are a few examples.
users.confuser=bob auth_type=ldap service=wui,sshd : allow map_to_user admin user=carol auth_type=ldap service=wui : allow map_to_user admin user=dave auth_type=ldap service=wui : allow map_to_user monitor :denyusers.confuser=bob auth_type=ldap service=wui,sshd : allow map_to_user admin user=carol auth_type=ldap service=wui : allow map_to_user admin user=dave auth_type=ldap service=wui : allow map_to_user monitor :denyYou can also allow access to all users in an AD group. Here, we give
adminaccess to all users in the AD groupaloha-admins. We givemonitoraccess to all users in the AD groupaloha-readonly.users.conftextgroup=aloha-admins auth_type=ldap : allow map_to_user admingroup=aloha-readonly auth_type=ldap : allow map_to_user monitor:denyusers.conftextgroup=aloha-admins auth_type=ldap : allow map_to_user admingroup=aloha-readonly auth_type=ldap : allow map_to_user monitor:denySet
:denyas the last entry in the file. HAProxy ALOHA evaluates entries from top to bottom. All entries after:denywill be ignored. -
To make your changes persistent after a reboot, click the Setup tab. Then click Save under Configuration.
The
configuration was successfully savedmessage displays.
You can also launch the following command from a terminal:
nixsudo config savenixsudo config saveYou can now sign in to HAProxy ALOHA with your Active Directory credentials. For example, with username
boband passwordbobs-password.
Test your configuration Jump to heading
Before you allow your LDAP users to log in, you should test a PAM configuration before you apply it.
-
Check that your configuration is parsed correctly:
nixsudo test_pam_user_map check_config -f /etc/security/users.confnixsudo test_pam_user_map check_config -f /etc/security/users.confoutputChecking config file /etc/security/users.conf Config file /etc/security/users.conf parsed successfullyoutputChecking config file /etc/security/users.conf Config file /etc/security/users.conf parsed successfully -
Simulate a local user logging in through
ssh:nixsudo test_pam_user_map check_pam_auth -f /etc/security/users.conf check_config -u bob -s sshd -t ldapnixsudo test_pam_user_map check_pam_auth -f /etc/security/users.conf check_config -u bob -s sshd -t ldapoutputtextChecking PAM access for user bobResult: auth_type=ldap allow=1 matched=1 map_to_user=adminPAM: access grantedoutputtextChecking PAM access for user bobResult: auth_type=ldap allow=1 matched=1 map_to_user=adminPAM: access granted -
Test your LDAP configuration with a real user and a real password:
nixsudo test_pam_user_map check_login_pass -f /etc/security/users.conf -u bob -p bobs-password -s sshd -t ldapnixsudo test_pam_user_map check_login_pass -f /etc/security/users.conf -u bob -p bobs-password -s sshd -t ldapoutputtextValidating user=bob password=*** service=sshdPAM user has been set to adminuser/password validated successfullyoutputtextValidating user=bob password=*** service=sshdPAM user has been set to adminuser/password validated successfullyTo troubleshoot errors, launch
nslcdin debug mode in an HAProxy ALOHA terminal:nixsudo service nslcd stopsudo nslcd -d -nnixsudo service nslcd stopsudo nslcd -d -nThen, in a separate terminal, try the failed command again.
Enable LDAP over SSL Jump to heading
You can enable LDAP over SSL (LDAPS) to secure the communication between the LDAP server and HAProxy ALOHA. You’ll need an SSL/TLS server certificate, which you can import into the LDAP server.
For information on how to export and import a certificate on Windows Server, see the guide Exporting the LDAPS Certificate and Importing for use with AD DS. We’ll outline the steps here. We assume you already have an SSL/TLS server certificate that has a common name (CN field) matching your Windows Server hostname.
Create a test certificate
For creating a test certificate, try minica. Then, to convert a .pem file to .pfx, use this openssl command:
nix
nix
On your Windows Server AD domain controller:
-
From a PowerShell terminal, run
mmc. This opens a Management Console window. -
In the Management Console window, click File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
-
Add
Certificates. For the certificates to manage, selectService account. -
Choose the computer to manage. If you’re on the Active Directory domain controller, choose the local computer.
-
For the service account to manage, select
Active Directory Domain Services, then click Finish. -
On the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, click OK.
-
Expand
Certificates - Services (Active Directory Domain Services), then clickNTDS\Personal. -
Right-click
NTDS\Personal, click All Tasks, and then click Import. -
Browse to and import your SSL/TLS server certificate and key file (
.pfx) into theNTDS/Personalstore.Active Directory is now configured for LDAP over SSL.
On HAProxy ALOHA:
-
If your HAProxy ALOHA host is a virtual appliance instead of hardware, you need to create an additional partition large enough to contain the files.
-
Attach a new hard disk to the virtual machine. It should be 30 GB or larger. See the documentation for your hypervisor or cloud service.
-
Power on your HAProxy ALOHA Virtual Appliance.
-
Log in to your HAProxy ALOHA web UI as an administrator. The web UI runs at port 4444.
-
Select the Tools tab, then edit the file
/etc/config.rcthrough the File Manager. Add the following directives at the end of theservice systemsection, then click Save:textapp_auto_mountapp_auto_formatapp_device_size 30000000000textapp_auto_mountapp_auto_formatapp_device_size 30000000000where:
app_auto_mountautomatically mounts the partition on/app.app_auto_formatautomatically formats the/apppartition, if needed.app_device_size <Size in bytes>specifies the size in bytes of the/apppartition. Here we set it to 30 GB.
-
Select the Setup tab, then click Save to save your modifications.
-
Restart HAProxy ALOHA by going to the Setup tab and clicking Reboot.
-
-
Launch a terminal from the web UI’s Tools tab.
-
Add the directory
/app/caand set its owner and group tonobody, which is the user account that thenslcdservice runs as. Callchmodwithg+sto set thesetgidbit so that files added to the directory later will inherit thenobodygroup.nixsudo mkdir /app/casudo chown -R nobody:nobody /app/casudo chmod g+s /app/canixsudo mkdir /app/casudo chown -R nobody:nobody /app/casudo chmod g+s /app/ca -
From the Tools tab, use the file explorer to upload the CA certificate file that corresponds to your SSL/TLS server certificate into the
/app/cadirectory. That will allow HAProxy ALOHA to trust the server certificate. If you’re usingminica, this isminica.pem. -
In the Services tab, click the [advanced mode] link, then edit the
nslcdconfiguration.
The content of the
/etc/nslcd.confNTP configuration file displays. -
Make the following changes:
-
Change the
uridirective to use theldaps://scheme.nslcd.conftexturi ldaps://dc1.mydomain.com/nslcd.conftexturi ldaps://dc1.mydomain.com/ -
Set
tls_cacertfileto the file path of your CA.pemfile.nslcd.conftexttls_cacertfile /app/ca/<your_CA_pem_file>.pemnslcd.conftexttls_cacertfile /app/ca/<your_CA_pem_file>.pem
-
-
Apply your changes to the
nslcdservice. Then, restart thenslcdservice. -
Test your LDAP configuration with a real user and a real password:
nixsudo test_pam_user_map check_login_pass -f /etc/security/users.conf -u bob -p bobs-password -s sshd -t ldapnixsudo test_pam_user_map check_login_pass -f /etc/security/users.conf -u bob -p bobs-password -s sshd -t ldapoutputtextValidating user=bob password=*** service=sshdPAM user has been set to adminuser/password validated successfullyoutputtextValidating user=bob password=*** service=sshdPAM user has been set to adminuser/password validated successfullyTo troubleshoot errors, launch
nslcdin debug mode in an HAProxy ALOHA terminal:nixsudo service nslcd stopsudo nslcd -d -nnixsudo service nslcd stopsudo nslcd -d -nThen, in a separate terminal, try the failed command again.
Troubleshooting Jump to heading
If the message # access denied using ssh, allowed when using login, displays, check the following:
-
The
AllowGroupsdirective is commented out in/etc/ssh/sshd_config.nixsudo grep -i AllowGroups /etc/ssh/sshd_confignixsudo grep -i AllowGroups /etc/ssh/sshd_configoutput# AllowGroups adm usersoutput# AllowGroups adm usersIf this directive isn’t commented out, check that your users’ groups are allowed:
nixsudo getent groupnixsudo getent group -
Check that
UsePAMis set toyesin/etc/ssh/sshd_config.nixsudo grep UsePAM /etc/ssh/sshd_confignixsudo grep UsePAM /etc/ssh/sshd_configoutputUsePAM yesoutputUsePAM yes
Limitations Jump to heading
- When using SCP, user remapping doesn’t work.
- When using SSH keys, user remapping doesn’t work (but key-based authentication does).
- You can’t change the password of an LDAP user using HAProxy ALOHA. If you need to do so, use the tools provided with your LDAP server.
See also Jump to heading
- For complete information on configuring the
nslcdservice, see the Local LDAP name service daemon man page at the Linux website.