Global Profiling Engine
Configure real-time aggregation of stick table data
This page applies to:
- HAProxy Enterprise - all versions
The Global Profiling Engine collects real-time stick table data from all HAProxy Enterprise nodes in the cluster. It then aggregates that data and pushes it back to all of the nodes.
For example, if LoadBalancer1 receives two requests and LoadBalancer2 receives three requests, the Global Profiling Engine will sum those numbers to get a total of five, then push that to both LoadBalancer1 and LoadBalancer2. This is helpful for an active/active load balancer configuration wherein the nodes need to share client request information to understand activity across the cluster accurately.
The aggregated data doesn’t overwrite the data on the load balancer nodes. Instead, it is pushed to secondary stick tables with, for example, a suffix of .agg. You would use a fetch method to retrieve the aggregated data and perform an action, like rate limiting.
Stick table data is transferred between the HAProxy Enterprise servers and the Global Profiling Engine server using the peers protocol, a protocol created specifically for this purpose. You must configure which servers should participate, both on the Global Profiling Engine server and on each HAProxy Enterprise node.
Configure HAProxy Enterprise nodes Jump to heading
An HAProxy Enterprise node must be configured to share its stick table data with the Global Profiling Engine server. Once aggregated, the profiling engine sends the data back to each node, which is stored in a new stick table.
Follow these steps on each load balancer:
-
Edit the file
/etc/hapee-3.2/hapee-lb.cfg. -
In the
globalsection of the file, add thelocalpeerdirective specifying the load balancer host name:hapee-lb.cfghaproxyglobal...# By setting this, you are directing HAProxy Enterprise to use the server line# that specifies this name as the local node.localpeer enterprise1hapee-lb.cfghaproxyglobal...# By setting this, you are directing HAProxy Enterprise to use the server line# that specifies this name as the local node.localpeer enterprise1 -
Add a
peerssection.hapee-lb.cfghaproxypeers mypeers# This is the address and port that the load balancer will receive aggregated data from the GPE serverbind 0.0.0.0:10000# The local HAProxy Enterprise node hostname defined by one of the following:# 1) the value provided when the load balancer process is started with the -L argument# 2) the localpeer name from the global section of the load balancer configuration (suggested method)# 3) the hostname as returned by the system hostname command (default)server enterprise1# The Global Profiling Engine# If you run GPE on the same server, use a different port hereserver gpe 192.168.50.40:10000# stick tables definitionstable request_rates type ip size 100k expire 30s store http_req_rate(10s)table request_rates.agg type ip size 100k expire 30s store http_req_rate(10s)hapee-lb.cfghaproxypeers mypeers# This is the address and port that the load balancer will receive aggregated data from the GPE serverbind 0.0.0.0:10000# The local HAProxy Enterprise node hostname defined by one of the following:# 1) the value provided when the load balancer process is started with the -L argument# 2) the localpeer name from the global section of the load balancer configuration (suggested method)# 3) the hostname as returned by the system hostname command (default)server enterprise1# The Global Profiling Engine# If you run GPE on the same server, use a different port hereserver gpe 192.168.50.40:10000# stick tables definitionstable request_rates type ip size 100k expire 30s store http_req_rate(10s)table request_rates.agg type ip size 100k expire 30s store http_req_rate(10s)Inside it:
-
Define a
bindline to set the IP address and port at which this node should receive data back from the Global Profiling Engine server. In this example, thebinddirective listens on all IP addresses at port 10000 and receives aggregated data. -
Define a
serverline for the current load balancer server. The server name value is important because it must match the name you set in the Global Profiling Engine server’s configuration for the correspondingpeerline. The hostname may be one of the following, in order of precedence:- the value provided with the
-Largument specified on the command line used to start the load balancer process - the
localpeername specified in theglobalsection of the load balancer configuration (this method is used in this example) - the host name returned by the system
hostnamecommand. This is the default, but we recommend using one of the other two methods
In this example, the local HAProxy Enterprise node is listed with only its hostname,
enterprise1. It isn’t necessary to specify its IP address and port. - the value provided with the
-
Define a
serverline for the Global Profiling Engine server. Set its IP address and port. The name you set here is also important; it must match the correspondingpeerline in the Global Profiling Engine server’s configuration. -
Define stick tables. For each one, add a duplicate line where the table name has the suffix
.agg. In this example, the non-aggregated stick tablerequest_rateswill store current HTTP request rates. The stick tables record the rate at which clients make requests over 10 seconds. We clear out stale records after 30 seconds by setting theexpireparameter on the stick table. Thetypeparameter sets the key for the table, which in this case is an IP address. The stick tablerequest_rates.aggreceives its data from the Global Profiling Engine. Its suffix,.agg, will match the profiling engine’s configuration.
localpeer definition
If you receive an error for your load balancer configuration that looks like the following after specifying the name for your load balancer on the
serverline:text[WARNING] (6125) : config : Removing incomplete section 'peers mypeers' (no peer named 'enterprise1')text[WARNING] (6125) : config : Removing incomplete section 'peers mypeers' (no peer named 'enterprise1')Specify your hostname value for
localpeerin yourglobalsection:hapee-lb.cfghaproxygloballocalpeer enterprise1hapee-lb.cfghaproxygloballocalpeer enterprise1This global setting is required in cases where your hostname (retrieved using the system
hostnamecommand) is different from your desired peer name. Be sure to update your GPE configuration to use the name you specify as thelocalpeername, as well as update your load balancer configuration to reference that name on theserverline for your load balancer in yourpeerssection. -
-
Add directives to your frontend, backend, or listen sections that populate the non-aggregated stick tables with data.
Below, the
http-request track-sc0line adds request rate information for each client that connects to the load balancer, using the client’s source IP address (src) as the key in the stick table.hapee-lb.cfghaproxyfrontend fe_mainbind :80default_backend webservers# add records to the stick table using the client's# source IP address as the table keyhttp-request track-sc0 src table mypeers/request_rateshapee-lb.cfghaproxyfrontend fe_mainbind :80default_backend webservers# add records to the stick table using the client's# source IP address as the table keyhttp-request track-sc0 src table mypeers/request_rates -
Add directives that read the aggregated data returned from the Global Profiling Engine server. That data is stored in the table with the suffix
.agg.Below, the
http-request denyline rejects clients that have a request rate greater than 1000. The client’s request rate is an aggregate amount calculated from all active load balancers. Note that this line reads data from therequest_rates.aggtable.hapee-lb.cfghaproxy# perform actions like rate limitinghttp-request deny deny_status 429 if { sc_http_req_rate(0,mypeers/request_rates.agg) gt 1000 }hapee-lb.cfghaproxy# perform actions like rate limitinghttp-request deny deny_status 429 if { sc_http_req_rate(0,mypeers/request_rates.agg) gt 1000 } -
Restart HAProxy Enterprise.
nixsudo systemctl restart hapee-3.2-lbnixsudo systemctl restart hapee-3.2-lb
Configure the Global Profiling Engine Jump to heading
The Global Profiling Engine server collects stick table data from HAProxy Enterprise load balancers in your cluster, but you must set which load balancers will be allowed to participate by listing them in the configuration file.
Use dynamic configuration Jump to heading
This section applies to:
- HAProxy Enterprise - GPE version 1.0 (
hapee-extras-gpe10package or newer)
Load balancers can connect to the GPE server without you adding them explicitly to the GPE configuration file. Include the dynamic-peers directive in either:
- the
aggregationssection to enable it for only that section. - the
globalsection to enable it for multipleaggregationssections.
For example, to set dynamic-peers in an aggregations section:
-
On the Global Profiling Engine server, edit the file
/etc/hapee-extras/hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfg. Add anaggregationssection that includesdynamic-peers:hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobal# Enables the Global Profiling Engine APIstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations data# set how to map non-aggregated to aggregated stick tablesfrom any to .agg# the profiling engine listens at this addresspeer gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 local# register load balancer on the flydynamic-peershapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobal# Enables the Global Profiling Engine APIstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations data# set how to map non-aggregated to aggregated stick tablesfrom any to .agg# the profiling engine listens at this addresspeer gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 local# register load balancer on the flydynamic-peers -
Optional: If you have multiple
aggregationssections, which is useful for serving multiple clusters of load balancers, then you can simplify your setup by setting abinddirective in theglobalsection instead of setting apeerline with thelocalkeyword in eachaggregationssection. This sets the address at which to listen for incoming stick table data.hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobal# Enables the Global Profiling Engine APIstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockbind 0.0.0.0:10000aggregations data# set how to map non-aggregated to aggregated stick tablesfrom any to .agg# register load balancer on the flydynamic-peershapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobal# Enables the Global Profiling Engine APIstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockbind 0.0.0.0:10000aggregations data# set how to map non-aggregated to aggregated stick tablesfrom any to .agg# register load balancer on the flydynamic-peersIf you do this, then on the load balancers the
peerline for the GPE server must use the same name as theaggregationssection. Here, the name isdata.hapee-lb.cfghaproxypeers mypeerspeer data 192.168.56.26:10000peer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000...hapee-lb.cfghaproxypeers mypeerspeer data 192.168.56.26:10000peer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000... -
Restart the Global Profiling Engine service:
nixsudo systemctl restart hapee-extras-gpenixsudo systemctl restart hapee-extras-gpeRestart after modifying tables
Whenever you make a change to your stick table definitions, such as to add new counters to the
storeargument or change theexpireargument, restart the Global Profiling Engine service for it to take effect.
Use static configuration Jump to heading
You can specify the IP address of each load balancer that is allowed to connect:
-
On the Global Profiling Engine server, edit the file
/etc/hapee-extras/hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfg.In the
aggregationssection, add apeerline for the Global Profiling Engine itself and for each HAProxy Enterprise node. Each peer’s name (e.g.enterprise1) should match the name you set in the HAProxy Enterprise configuration, since that is how the profiling engine validates the peer.Peer names
Be sure that the peer names you specify in the GPE server’s configuration match exactly the names you specified in your load balancer configuration. For example, the following load balancer configuration sets the load balancer’s
localpeername toenterprise1and we reference this name again in thepeerssection:hapee-lb.cfghaproxygloballocalpeer enterprise1...peers mypeersbind 0.0.0.0:10000server enterprise1...hapee-lb.cfghaproxygloballocalpeer enterprise1...peers mypeersbind 0.0.0.0:10000server enterprise1...As such, it must appear in the GPE server’s configuration as
enterprise1in order for GPE to make connection to the load balancer.hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobal# Enables the Global Profiling Engine APIstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations data# set how to map non-aggregated to aggregated stick tablesfrom any to .agg# the profiling engine listens at this addresspeer gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 local# the load balancers listen at these addressespeer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobal# Enables the Global Profiling Engine APIstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations data# set how to map non-aggregated to aggregated stick tablesfrom any to .agg# the profiling engine listens at this addresspeer gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 local# the load balancers listen at these addressespeer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000In this example:
-
The Global Profiling Engine API provides a programmable API, which listens at the socket
/var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sock. Thestats socketdirective enables a CLI that lets you view data that the aggregator has stored. -
In the
aggregationssection, thefromline defines how non-aggregated stick tables map to aggregated stick tables, and what the suffix for the aggregated stick tables should be. The keywordanymeans that any stick table found will be aggregated. Aggregated data is pushed to tables with the same name, but ending with the suffix.agg. In the example, the engine expects stick tables to be named likerequest_ratesand it will push aggregated data torequest_rates.agg.You can also use a more specific mapping. In the example below, the engine expects stick tables to be named like
request_rates.nonaggand it will push aggregated data torequest_rates.agg. Stick tables without the.nonaggsuffix will be ignored.hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyfrom .nonagg to .agghapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyfrom .nonagg to .agg -
The
peerline with thelocalargument indicates the local GPE server. -
HAProxy Enterprise
peerlines must use the same name you set on theserverline in the HAProxy Enterprise configuration (e.g.enterprise1), and they must specify the IP addresses and ports where the load balancers are receiving aggregated data.
-
-
Restart the Global Profiling Engine service:
nixsudo systemctl restart hapee-extras-gpenixsudo systemctl restart hapee-extras-gpeRestart after modifying tables
Whenever you make a change to your stick table definitions, such as to add new counters to the
storeargument or change theexpireargument, restart the Global Profiling Engine service for it to take effect.
Verify your setup Jump to heading
Check that the Global Profiling Engine and load balancers are setup correctly by utilizing their APIs.
-
On the load balancer, call the Runtime API function
show peersto check that the Global Profiling Engine is listed and that itslast_statusisESTA(established):Below, the
show peerscommand lists connected peers:nixecho "show peers" | sudo socat stdio unix-connect:/var/run/hapee-3.2/hapee-lb.sock | head -2nixecho "show peers" | sudo socat stdio unix-connect:/var/run/hapee-3.2/hapee-lb.sock | head -2outputtext0x5651d4a03010: [07/Jul/2021:17:02:30] id=mypeers disabled=0 flags=0x2213 resync_timeout=<PAST> task_calls=920x5651d4a06540: id=gpe(remote,active) addr=192.168.50.40:10000 last_status=ESTA last_hdshk=2m17soutputtext0x5651d4a03010: [07/Jul/2021:17:02:30] id=mypeers disabled=0 flags=0x2213 resync_timeout=<PAST> task_calls=920x5651d4a06540: id=gpe(remote,active) addr=192.168.50.40:10000 last_status=ESTA last_hdshk=2m17s -
On the load balancer, call the Runtime API function
show tableto see data in non-aggregated and aggregated stick tables.Below, we view data in the stick table named
request_rates.agg:nixecho "show table mypeers/request_rates.agg" | sudo socat stdio unix-connect:/var/run/hapee-3.2/hapee-lb.socknixecho "show table mypeers/request_rates.agg" | sudo socat stdio unix-connect:/var/run/hapee-3.2/hapee-lb.sockoutputtext# table: mypeers/request_rates.agg, type: ip, size:102400, used:10x7fc0e401fb80: key=192.168.50.1 use=0 exp=28056 http_req_rate(10000)=5outputtext# table: mypeers/request_rates.agg, type: ip, size:102400, used:10x7fc0e401fb80: key=192.168.50.1 use=0 exp=28056 http_req_rate(10000)=5 -
On the Global Profiling Engine server, call the
show aggrsfunction to see load balancers that are registered as peers. Astateof0x7means a successful connection. If you see a state of0xffffffff, that means that a connection was not successful. Often, this is caused by the peer names not matching between the Global Profiling Engine’s configuration and the HAProxy Enterprise configuration.Below, the
show aggrscommand shows that the peer namedenterprise1has connected:nixecho "show aggrs" | sudo socat stdio /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.socknixecho "show aggrs" | sudo socat stdio /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockoutputtextaggregations datapeer 'enterprise1'(0) sync_ok: 1 accept: 1(last: 6080) connect: 1(last: 16086) state: 0x7 sync_state: 0x3sync_req_cnt: 0 sync_fin_cnt: 0 sync_cfm_cnt: 0outputtextaggregations datapeer 'enterprise1'(0) sync_ok: 1 accept: 1(last: 6080) connect: 1(last: 16086) state: 0x7 sync_state: 0x3sync_req_cnt: 0 sync_fin_cnt: 0 sync_cfm_cnt: 0
Optional: Bind outgoing connections to an interface Jump to heading
If the server where you are running the Global Profiling Engine has multiple network interfaces, you can configure the engine to bind to a specific one for outgoing data sent to HAProxy Enterprise servers.
To bind outgoing connections to a specific address, use the source directive in the global section.
IPv4 examples
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
The port is optional. It defaults to 0 for random ports.
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
IPv6 examples
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
The port is optional. It defaults to 0 for random ports.
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxy
GPE with session persistence Jump to heading
This section applies to:
- HAProxy Enterprise 2.9r1
A special situation arises when you want to use the Global Profiling Engine to sync session persistence data across load balancers. Session persistence uses a stick table to track which server a client was routed to initially and from then on continues to route that client to the same server.
-
For example, consider the
backendbelow that enables session persistence, but without GPE:hapee-lb.cfghaproxybackend serversstick-table type ip size 1m expire 30mstick on srcserver s1 192.168.0.10:80 checkserver s2 192.168.0.11:80 checkhapee-lb.cfghaproxybackend serversstick-table type ip size 1m expire 30mstick on srcserver s1 192.168.0.10:80 checkserver s2 192.168.0.11:80 check -
We need to make the following changes to the
backend:- Remove the
stick-tableline. - Make the
stick ondirective reference thesessionstable in thepeerssection namedmypeers. - By default, each load balancer can arrange the servers differently. However, we need to ensure consistent server IDs across all load balancers, so we use the
idargument to set the IDs explicitly.
hapee-lb.cfghaproxybackend serversstick on src table mypeers/sessionsserver s1 192.168.0.10:80 check id 1server s2 192.168.0.11:80 check id 2hapee-lb.cfghaproxybackend serversstick on src table mypeers/sessionsserver s1 192.168.0.10:80 check id 1server s2 192.168.0.11:80 check id 2 - Remove the
-
Move the
stick-tabledefinition to thepeerssection:hapee-lb.cfghaproxypeers mypeersbind 0.0.0.0:10000server enterprise1server gpe 192.168.50.40:10000table sessions type ip size 1m expire 30m store server_id,server_keytable sessions.agg type ip size 1m expire 30m store server_id,server_key write-to mypeers/sessionshapee-lb.cfghaproxypeers mypeersbind 0.0.0.0:10000server enterprise1server gpe 192.168.50.40:10000table sessions type ip size 1m expire 30m store server_id,server_keytable sessions.agg type ip size 1m expire 30m store server_id,server_key write-to mypeers/sessionsIn this example:
- We have moved the stick table to the
peerssection and named itsessions. You must set itsstoreargument toserver_id,server_key. - A table named
sessions.aggsyncs session persistence data to GPE, which then syncs it to all load balancers. The aggregate table must set thewrite-toargument so that the data is written back to thesessionstable. Thewrite-toparameter allows remote load balancers to update the localsessionstable with session persistence data.
- We have moved the stick table to the
-
Restart HAProxy Enterprise.
nixsudo systemctl restart hapee-3.2-lbnixsudo systemctl restart hapee-3.2-lb -
Make this exact change on the other HAProxy Enterprise server, then restart it.
-
On the GPE server, restart the Global Profiling Engine service:
nixsudo systemctl restart hapee-extras-gpenixsudo systemctl restart hapee-extras-gpe
Multi-level setup Jump to heading
You can aggregate stick tables from other Global Profiling Engines, which allows you to aggregate stick tables across different data centers, for example.
We will consider the following setup:
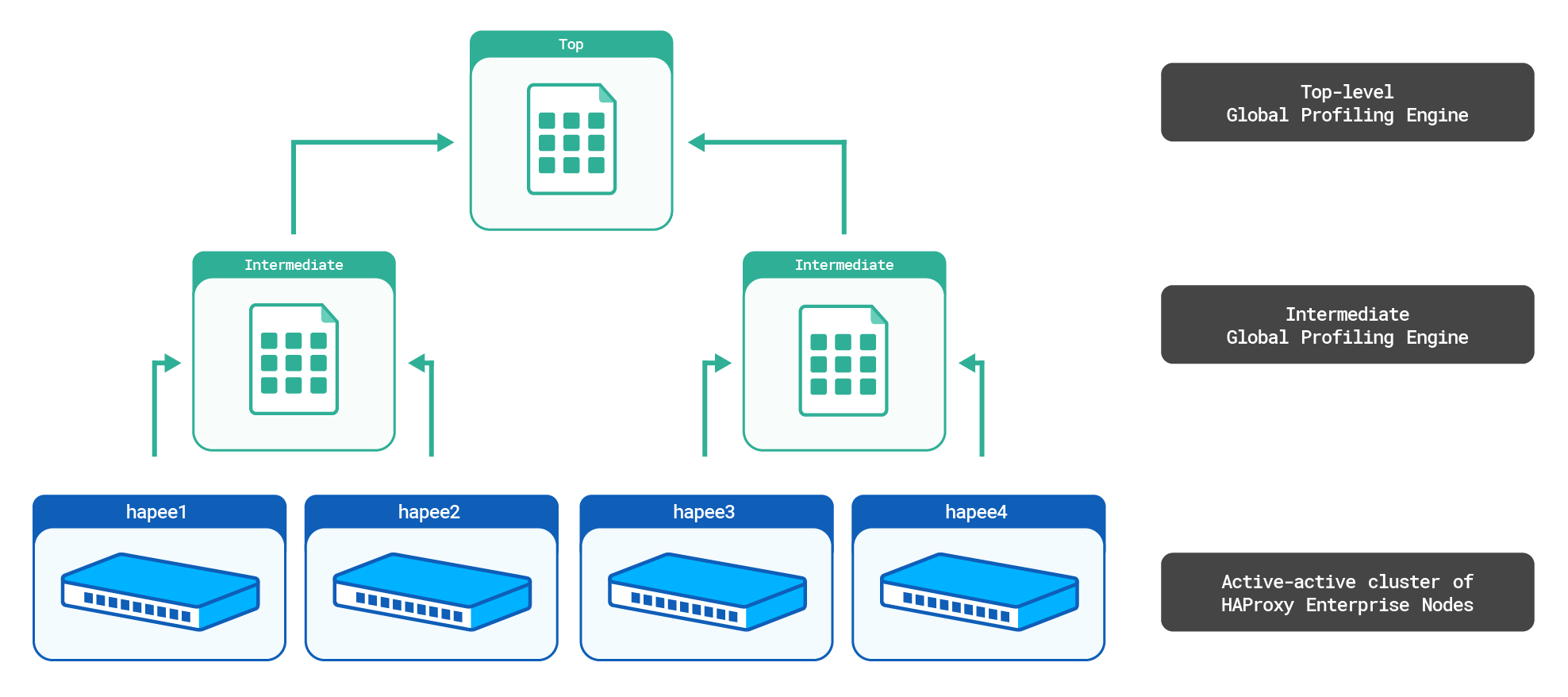
The top-level aggr3 Global Profiling Engine will sum the counters from the intermediate aggr1 and aggr2 aggregate stick tables. It will then send the top-level aggregate stick table to all HAProxy Enterprise nodes.
You can also host multiple top-level servers for high availability. In that case, intermediate servers simply push their data to both. See below for details.
Configure the top-level Global Profiling Engine Jump to heading
Follow these steps on the server you wish to be the top-level Global Profiling Engine.
-
Edit the file
/etc/hapee-extras/hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfg.hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations toplevelfrom .intermediate to .aggpeer top-gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer intermediate-gpe1 192.168.56.111:10000 downpeer intermediate-gpe2 192.168.56.112:10000 downhapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations toplevelfrom .intermediate to .aggpeer top-gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer intermediate-gpe1 192.168.56.111:10000 downpeer intermediate-gpe2 192.168.56.112:10000 down-
The current server has the
localkeyword set on itspeerline. -
In this example, two other Global Profiling Engine servers, intermediate-gpe1 and intermediate-gpe2, are listed with the
downkeyword, which means that they are one level down from the top. -
The top-level Global Profiling Engine will aggregate stick table data from the intermediate servers. Their stick tables should have the
.intermediatesuffix. -
The top-level Global Profiling Engine will push aggregated data back to the intermediate servers. The globally aggregated stick tables should have the
.aggsuffix.
-
Configure the intermediate Global Profiling Engines Jump to heading
Follow these steps on the servers you wish to be the intermediate-level Global Profiling Engines.
-
Edit the file
/etc/hapee-extras/hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfg.intermediate-gpe1
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations myaggrfrom any to .intermediateforward .aggpeer intermediate-gpe1 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer top-gpe 192.168.56.113:10000 uppeer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations myaggrfrom any to .intermediateforward .aggpeer intermediate-gpe1 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer top-gpe 192.168.56.113:10000 uppeer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000intermediate-gpe2
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations myaggrfrom any to .intermediateforward .aggpeer intermediate-gpe2 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer top-gpe 192.168.56.113:10000 uppeer enterprise3 192.168.50.51:10000peer enterprise4 192.168.50.52:10000hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations myaggrfrom any to .intermediateforward .aggpeer intermediate-gpe2 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer top-gpe 192.168.56.113:10000 uppeer enterprise3 192.168.50.51:10000peer enterprise4 192.168.50.52:10000-
The
fromline aggregates stick table data to tables with the suffix.intermediate. You can disable sending data to the top-level aggregators by addingno-ascendto this line. Disable sending aggregated data to the load balancers downstream from the intermediate aggregators by addingno-feedback. -
The current server has the
localkeyword set on itspeerline. -
The upper-level Global Profiling Engine peer is denoted by the
upkeyword. -
Each intermediate Global Profiling Engine is aware of only the HAProxy Enterprise nodes it manages and of the top-level Global Profiling Engine.
-
The intermediate-level Global Profiling Engines will aggregate stick table data from the HAProxy Enterprise servers.
-
The
forwardline relays the top-level server’s.aggstick tables to the HAProxy Enterprise servers. -
The intermediate-level Global Profiling Engines will push aggregated data back to the HAProxy Enterprise servers. The aggregated stick tables should have the
.aggsuffix.
-
Configure for high availability Jump to heading
To create a highly available setup, you can have multiple top-tier servers. In this configuration, the top-tier servers use the group parameter to link the intermediate servers together into a single entity. If either top-tier server goes down, the other still receives aggregated results from the intermediate group entity. If either intermediate server goes down, the other intermediate server continues to compute and aggregate results to send to the top-tier servers.
Info
Grouping the intermediate aggregators requires that the aggregators be active at the same time. Consequently, the high availability configuration imposes greater network traffic and CPU demands on the peers, whether serving as sending or receiving peers, and on the load balancer nodes.
-
The top-tier servers should each have the same configuration.
-
In the top-tier configurations, add the
groupparameter to the intermediate peerspeerdirectives.top-tier servers
Edit the file
/etc/hapee-extras/hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfg.hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations toplevelfrom .intermediate to .aggpeer top-gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer intermediate-gpe1 192.168.56.111:10000 down group 1peer intermediate-gpe2 192.168.56.112:10000 down group 1hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations toplevelfrom .intermediate to .aggpeer top-gpe 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer intermediate-gpe1 192.168.56.111:10000 down group 1peer intermediate-gpe2 192.168.56.112:10000 down group 1 -
On the intermediate peers, add the entry for the additional top-level server.
Edit the file
/etc/hapee-extras/hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfg.intermediate-gpe1
hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations myaggrfrom any to .intermediateforward .aggpeer intermediate-gpe1 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer top-gpe1 192.168.56.113:10000 uppeer top-gpe2 192.168.56.114:10000 uppeer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000hapee-gpe-stktagg.cfghaproxyglobalstats socket /var/run/hapee-extras/gpe-api.sockaggregations myaggrfrom any to .intermediateforward .aggpeer intermediate-gpe1 0.0.0.0:10000 localpeer top-gpe1 192.168.56.113:10000 uppeer top-gpe2 192.168.56.114:10000 uppeer enterprise1 192.168.50.41:10000peer enterprise2 192.168.50.42:10000
See also Jump to heading
- For complete information on the peers section syntax and usage, see Peers configuration reference.
- To set the local instance’s peer name, see localpeer reference.