Layer 4 (LVS)
Load balance UDP using the LB Layer4 tab
To load balance UDP services, use a Linux Virtual Server (LVS) load balancer in NAT mode to perform the load balancing at layer 4. In this scenario, responses from servers flow through HAProxy ALOHA (that is, not Direct Server Return).
Enable destination NAT Jump to heading
Configure LVS so that it translates the destination IP from the public IP on which HAProxy ALOHA listens to the backend server’s private IP.
-
In the web UI’s LB Layer4 tab, add the
mode natdirective to your existing configuration.haproxydirector web 10.0.0.3:8000 UDPbalance leastconnmode natserver web1 10.0.0.20:8000 weight 10 checkhaproxydirector web 10.0.0.3:8000 UDPbalance leastconnmode natserver web1 10.0.0.20:8000 weight 10 check -
Click OK and Apply.
-
Click on the Setup tab. In the Configuration section, click Save.
Enable source NAT Jump to heading
Create iptables NAT rules to translate the client’s source IP to the HAProxy ALOHA appliance’s IP.
There are two example configurations.
-
One network interface
text--------+-------- 10.0.0.0/24, VIPs, backend servers|| eth0+---------+| || ALOHA || |+---------+text--------+-------- 10.0.0.0/24, VIPs, backend servers|| eth0+---------+| || ALOHA || |+---------+ -
Two network interfaces
text--------+-------- 10.0.0.0/24, VIPs|| eth0+---------+| || ALOHA || |+---------+| eth1|--------+-------- 10.0.3.0/24, backend serverstext--------+-------- 10.0.0.0/24, VIPs|| eth0+---------+| || ALOHA || |+---------+| eth1|--------+-------- 10.0.3.0/24, backend serversInfo
In configurations having two network interfaces, if you have failover configured on one VIP, configure a VIP with failover on the other interface as well.
-
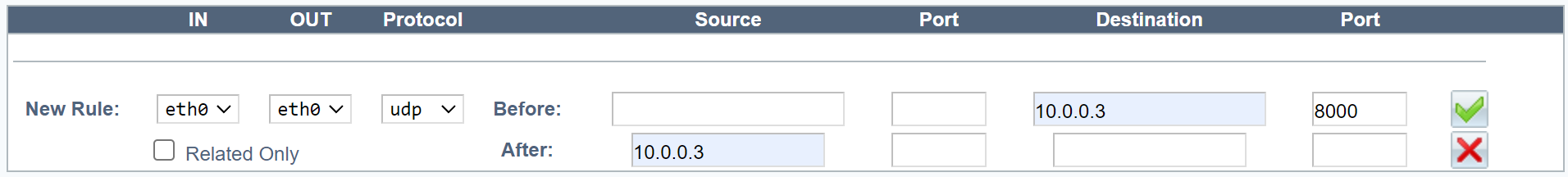
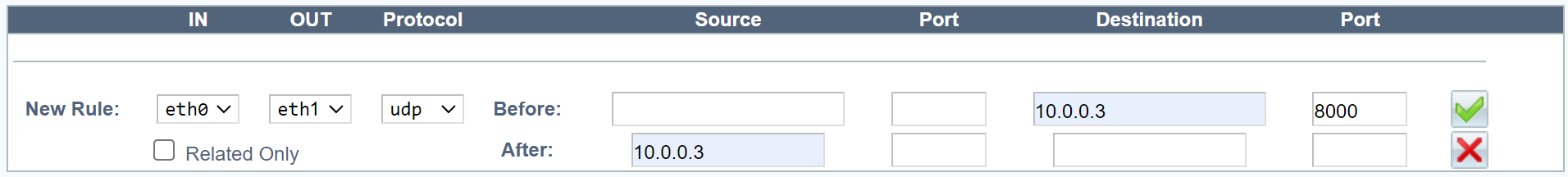
In the NAT tab, click Insert to add a new NAT rule.
-
In the New Rule area, fill in the fields as directed below.
Field Description IN Inbound network interface. OUT Outbound network interface. In a configuration with one network interface, this should be the same as the inbound interface. In a configuration with two interfaces, this interface should be different from the inbound interface. Protocol UDP. -
In the Before area, fill in the fields as directed below.
Field Value Example Source Blank Source port Blank Destination VIP address 10.0.0.3 Destination port UDP port or range 8000, or 50000-51000 -
In the After area, fill in the fields as directed below.
Field Value Example Source VIP address (Note: If you enter a local IP address, it cannot be shared between the members of a cluster.) 10.0.0.3 Source port Blank Destination Blank Destination port Blank -
Check your configuration.
- One network interface.
- Two network interfaces.
-
Click Add and Apply.
-
On the Setup tab, in the Configuration section, click Save.
Enable LVS connection tracking Jump to heading
NAT relies on the connection tracking information so that it can translate all of the packets in a session in the same way.
-
Click the Services tab.
-
Locate the lvs service and click Setup.
-
Enable connection tracking through the
conntrackkeyword.textservice lvs############ Linux Virtual Server, layer 3/4 load balancingconntracktextservice lvs############ Linux Virtual Server, layer 3/4 load balancingconntrack -
Click OK and then Close.
-
Locate the lvs service and click Restart.
-
Click on the Setup tab. In the Configuration section, click Save.
Do you have any suggestions on how we can improve the content of this page?